Summary
20 hours ago Matlableach mat lab code on leach algorithm - DSSZ An Improved Routing Algorithm Based on LEACH Protocol - IEEE. Leach multi-hop protocols MATLAB code, comment more, simple and understandable. Leach multi-hop protocols, in leach protocol based on modifications to achieve, for the cluster head node cannot directly communicate with the base station environment. One of the important problems for wireless sensor networks is increasing the network lifetime. Clustering is an efficient technique for prolonging the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. This papers propose a multihop clustering algorithm (MHC) for energy saving in wireless sensor networks. MHC selects the clusterheads according to the two parameters the remaining energy and node degree. Welcome to download section of LEACH Protocol in Wireless Sensor Network.In this page, you can find information on downloading LEACH protocol source code for your favorite simulator software application like NS-2, Matlab, C and OMNeT for your Thesis & Research Works.


This is a research project done in 2017 in University of Melbourne. It aims to make improvements on LEACH protocol, which is a cluster-based routing protocol in Wireless Sensor Network. The project is simulated by MATLAB.
Strategies
EMH-LEACH protocol is proposed to modify drawbacks of LEACH from three main aspects:
- change the homogeneous network model to heterogeneous network model;
- modify the Cluster Heads selection threshold formular in set-up phase (by considering the remaining energy of each node when selecting the Cluster Heads);
- change the single-hop transmission to multi-hop transmission between Cluster Heads and the Base Station (by considering the transmission distance when selecting the Cluster Heads).
Simulation and Performance Review
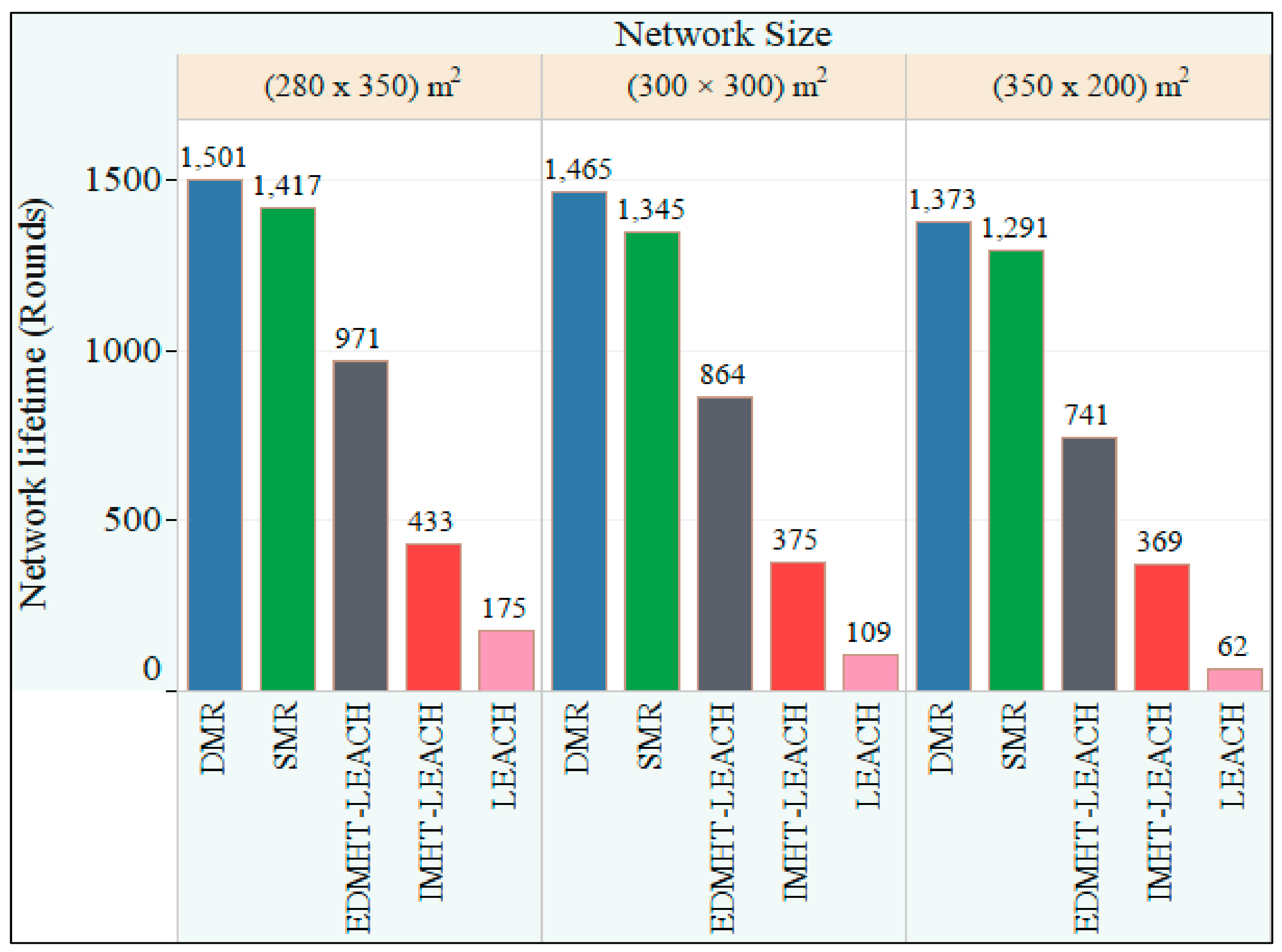
There are several performance metrics used here to evaluate the newly proposed EMH- LEACH:
Matlab Code Example
- The round number of the first dead node (FND): FND can be used to evaluate the stability of the network. Because when the first node dies, other nodes begin to die one after another. This means that fewer nodes are involved in gathering and forwarding data in the network, and the burden of them become heavier. The more work they do, the faster they die. This will impact the performance of the whole network.
- The round number of the half dead node (HND): HND can be used to evaluate the quality of the network. Because if in a small area, nodes are closed to each other, the data detected by adjacent nodes is likely to be similar. At this time, the performance of the whole network will not be impacted even if some nodes die. It only matters when quite a few nodes are not living any more.
- The alive nodes number per round: the sum of nodes remaining at the end of each turn can reflect the lifetime of the network, which is a straightforward way to measure the performance of the protocols.
- The distribution of alive nodes in the whole network when half nodes out of all are dead: from the distribution of alive nodes in the network, we can see whether the energy consumption of the WSN is balance or not. In the round of half nodes dead, if those dead nodes are located near the BS, this means that they are involved in too many data forwarding activities. On the other hand, if those dead nodes are located far away from the BS, this means that the data transmission distance for them is too long and they do not find the appropriate internal nodes to do the data forwarding for them. The ideal situation is that the distribution of those dead nodes is relatively even all over the network.